Abstract
Extracting the speech of participants in a conversation amidst interfering speakers and noise presents a challenging problem. In this paper, we introduce the novel task of target conversation extraction, where the goal is to extract the audio of a target conversation based on the speaker embedding of one of its participants. To accomplish this, we propose leveraging temporal patterns inherent in human conversations, particularly turn-taking dynamics, which uniquely characterize speakers engaged in conversation and distinguish them from interfering speakers and noise. Using neural networks, we show the feasibility of our approach on English and Mandarin conversation datasets. In the presence of interfering speakers, our results show an 8.19~dB improvement in signal-to-noise ratio for 2-speaker conversations and a 7.92~dB improvement for 2-4-speaker conversations
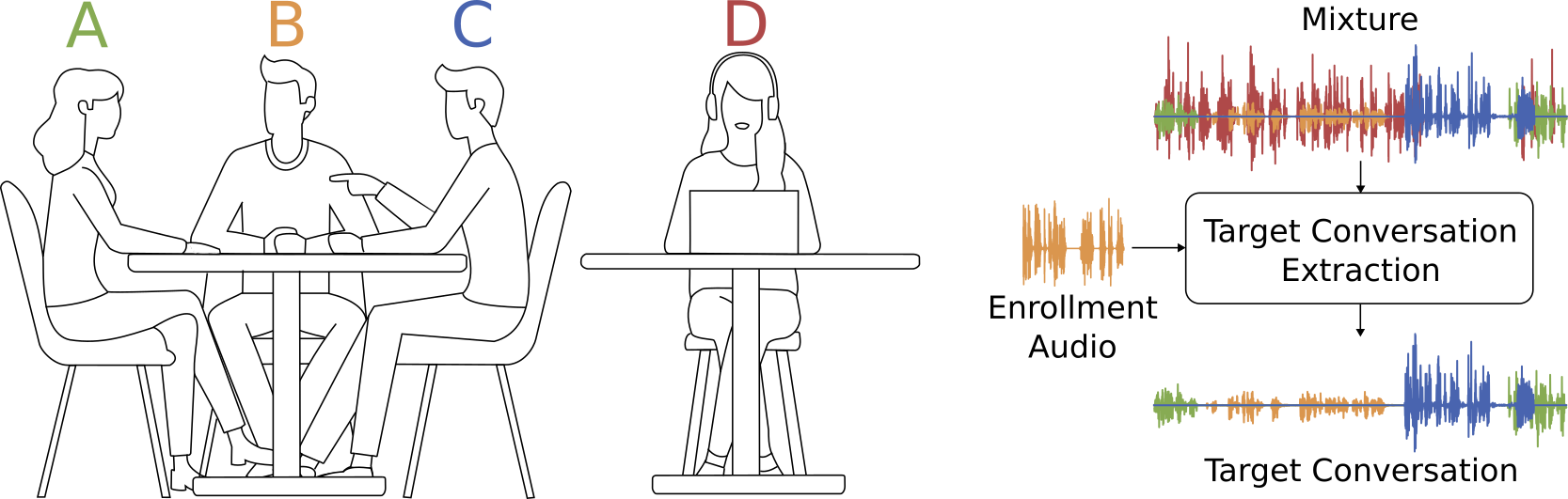
The goal of target conversation extraction in this illustration is as follows: given a clean enrollment audio or embedding for B, we want to extract audio for the conversation between A, B and C, amidst interference from speaker D.